Transition, Permaculture, and Slow Technology
Slow Tech referenced Preserving the Past to Serve the Future
A version of this article first appeared on the Mid-Atlantic Transition Hub (MATH) of Transition US, blog
Transition US has published Preserving the Past to Serve the Future https://www.transitionus.org/stories/preserving-past-serve-future-using-pre-fossil-fuel-technology-regional-waterways
OpEd News has published Preserving the Past to Serve the Future https://www.opednews.com/articles/Preserving-the-Past-to-Ser-by-Andrew-Willner-130731-538.html
Keene Transitions has re-published Preserving the Past to Serve the Future, https://keenetransition.wordpress.com/events-calendar/re-skilling-workshops/
The Permaculture Research Center has posted Preserving the Past to Serve the Future https://permaculturenews.org/2013/08/23/preserving-the-past-to-serve-the-future/
Resilience re-posted Preserving the Past to Serve the Future https://www.resilience.org/stories/2013-08-27/preserving-the-past-to-serve-the-future-using-pre-fossil-fuel-technology-on-regional-waterways

“Today, traditional knowledge is in danger and its disappearance would not only cause the loss of people’s capability to keep and pass on the artistic and natural heritage, but also of an extraordinary source of knowledge and cultural diversity from which the appropriate innovation solutions can be derived today and in the future.”
Slow Money is a movement to organize investors and donors to steer new sources of capital to small food enterprises, organic farms, and local food systems. The Slow Food movement aims to preserve cultural cuisine and in so doing to preserve the food plants and seeds, domestic animals and farming within an eco-region. It is also a social and political movement that resists the dehumanizing effects of fast food and corporate farming. Slow Tech is about the re-invigoration of heirloom technologies and traditional skills needed to thrive in a carbon-constrained future.
movement aims to preserve cultural cuisine and in so doing to preserve the food plants and seeds, domestic animals and farming within an eco-region. It is also a social and political movement that resists the dehumanizing effects of fast food and corporate farming. Slow Tech is about the re-invigoration of heirloom technologies and traditional skills needed to thrive in a carbon-constrained future.
Transition is the movement by which people are re-skilled in heirloom technologies. Permaculture gave birth to the Transition movement and offers guidance on how to use those skills to design resilient lives.  The ethics; earth care, people care, and fair share form the foundation for Permaculture and are also found in most traditional societies. Permaculture incorporates knowledge from cultures that have existed in balance with their environment for much longer than our consumer centered fossil fueled society. We should not ignore the positive accomplishments of modern times, but in the transition to a sustainable future, we need to consider values and concepts different from what has become the social norm.
The ethics; earth care, people care, and fair share form the foundation for Permaculture and are also found in most traditional societies. Permaculture incorporates knowledge from cultures that have existed in balance with their environment for much longer than our consumer centered fossil fueled society. We should not ignore the positive accomplishments of modern times, but in the transition to a sustainable future, we need to consider values and concepts different from what has become the social norm.
Slow Technology:
C. Milton Dixon, interviewed in The (Chicago) Examiner, May 2011, said:
“(high tech is) industrial technology and refers to things that are out of your control, as opposed to low technology, which is simple things done in a smart way. Low technology is using the intelligence of nature to accomplish tasks. High technology is buying an apple from the store; low technology is getting an apple from a tree you planted yourself. One of the big differences is in high technology you are disconnected from cause and effect relationships. So if you pollute through high technology, you may not feel the direct result. Low technology is connection because you are involved in the process and you are directly affected by the consequences.”
The idea of Slow Technology has its roots in the ideological movement called “appropriate technology,” a term coined by E.F. Schumacher in his book “Small is Beautiful,” first published in 1973. Slow or appropriate technology centers on ideas of proper scale: technology should be “people-centered.” “Slow technology as an ideology that extends  thoughtfulness about how devices shape our relationships to time, emotion and energy. Slow Technology is articulated in an article by two Swedish designers, Lars Hallnas and Johan Redstrom, who in 2001 described Slow Technology as “a design agenda for technology aimed at reflection and moments of mental rest rather than efficiency in performance.”
thoughtfulness about how devices shape our relationships to time, emotion and energy. Slow Technology is articulated in an article by two Swedish designers, Lars Hallnas and Johan Redstrom, who in 2001 described Slow Technology as “a design agenda for technology aimed at reflection and moments of mental rest rather than efficiency in performance.”
….. the central condition of empowering people to develop to the best of their abilities and to have freedom to succeed or fail based on their own efforts is critical. The appropriate technology movement has at its philosophical heart the desire to capacitate people of all walks of life to create (1) Meaningful Employment, (2) Comprehension of Technology, (3) Self-Reliance, and (4) Reduced Environmental Impacts.
Transition fosters and supports the revitalization of Slow Tech skills and Permaculture asks us to consider relearning the proficiency needed to reanimate wind mills, watermills, and sailing vessel while putting hand tools, levers, and blocks and tackle back into service.
Technology can be Slow in various ways:
- It takes time to learn how it works,
- It takes time to understand why it works the way it works,
- It takes time to apply it
- It takes time to see what it is
- and it takes time to find out the consequences of using it
 No woodworker’s first project is a chair, a house, a mill, or a boat. My first woodworking lesson was to take a rough piece of lumber, and using hand tools that (I sharpened) to shape it into a three dimensional absolutely square finished piece of wood. It took me a full day and I used every tool on my bench.
No woodworker’s first project is a chair, a house, a mill, or a boat. My first woodworking lesson was to take a rough piece of lumber, and using hand tools that (I sharpened) to shape it into a three dimensional absolutely square finished piece of wood. It took me a full day and I used every tool on my bench.
Once my practice was established I developed a method that worked for me. First I sat with a piece of tracing paper and did a rough sketch of the final product. Then I drew it full scale in three views. From that drawing I could determine what amount of wood was needed, where each joint would go, and how the pieces would transition from one to another to create an aesthetically pleasing whole. Then the sawing, planing, joinery, shaping, and finishing would take place. Each of those steps were learned by doing, learning from others, by using traditional references, and knowing that the dimensions and materials were appropriate for the final use.
another to create an aesthetically pleasing whole. Then the sawing, planing, joinery, shaping, and finishing would take place. Each of those steps were learned by doing, learning from others, by using traditional references, and knowing that the dimensions and materials were appropriate for the final use.
I was lucky both to have mentors, and to have the time to hone my skills first as a student, then an apprentice, and then as a resident woodworker at Peters Valley Craft Center in New Jersey. Peters Valley gave me the opportunity, and the time, to learn the business, practice my craft, and teach. It also was a community of like-minded professional potters, weavers, metal workers, and woodworkers that supported one  another. If we are to learn the skills necessary to survive and thrive in a post carbon world, more places like Peters Valley will be necessary, more experienced craft workers will have to open their shops to apprentices, and more people are going to have to be willing to take the time, resources, and effort to learn.
another. If we are to learn the skills necessary to survive and thrive in a post carbon world, more places like Peters Valley will be necessary, more experienced craft workers will have to open their shops to apprentices, and more people are going to have to be willing to take the time, resources, and effort to learn.
I left a “Deep Transition” course at Genesis Farm in New Jersey where we decided that one of the “take aways” was to look for streams in our home watersheds called “Mill Creek,” and streets in our towns called, “Mill Road.” In doing so we might find a mill converted to another use. I easily found at several Mill Creeks and one Saw Mill Creek in my watershed.
 Near a farm where I work part of the week In Clinton, NJ one mill is an art center and the other is operating as an exhibit. In Thompson PA the old grain mill is operational but abandoned. Many mills are currently used as educational tools by historical societies or operated as restaurants and shops rather than for the purposes for which they were built.
Near a farm where I work part of the week In Clinton, NJ one mill is an art center and the other is operating as an exhibit. In Thompson PA the old grain mill is operational but abandoned. Many mills are currently used as educational tools by historical societies or operated as restaurants and shops rather than for the purposes for which they were built.
Water mills are being built and rebuilt for grinding grain, pressing cider, as well as producing electricity for individually owned operations and nearby communities. Building, restoring, preserving, and actively using these technologies is key to preserving the past to serve the future. In order to support these efforts, Transition advocates must make alliances with historical societies who use these mills as educational tools but are not operating them for the purposes for which they were built; with restaurant owners and antique stores that are using the mills for a completely unrelated purposes; and to identify locations where mills can be built or rebuilt in order to re-skill the woodworkers, millwrights, and inform farmers about the advantages of water power for the future.
Commerce and water transport of farm and manufactured goods flourished for millennia before cheap fossil fuels became readily available. Short Sea Shipping: i.e. carrying freight that does not cross oceans, is having a resurgence particularly in Europe as more people build and rebuild ships for the transport of goods along coastal waters. The inland waters of the mid-Atlantic is a region where sailing cargo vessels may well be competitive right now for certain cargoes.
Erik Andrus’ Vermont Sail Freight Project is the most viable such project in The Mid-Atlantic region. The vessel Ceres, built on a farm near Lake Champlain will carry Vermont farm goods to New York City and ports in between, and return to Burlington with fair trade goods, like cocoa beans that have been delivered by sailing vessel to Brooklyn from the Caribbean.
vessel Ceres, built on a farm near Lake Champlain will carry Vermont farm goods to New York City and ports in between, and return to Burlington with fair trade goods, like cocoa beans that have been delivered by sailing vessel to Brooklyn from the Caribbean.
The Vermont Sail Freight Project is worthy of our support, but Transition advocates must encourage the owners of small sail freighters like the South Street Seaport’s Pioneer to put her back into that service for the part of the year she is not carrying passengers, and for other vessels like Clearwater to become pilots for the Slow Tech freight carriers of the future.
The Mid-Atlantic Transition Hub (MATH) of Transition US will support these efforts in the fall of 2013 by bringing together builders, millwrights, boat builders, woodworkers, crafts persons, and historical societies to participate in a Powered Down Waterways Reskilling Festival. Jim Kricker, preeminent restorer of traditional waterwheels, windmills and sailing vessels,  will anchor a two-day Reskilling Festival featuring demonstrations, talks, and hands-on instruction. Jim’s website, Rondout Woodworking is a valuable resource for locating working and restored mills.
will anchor a two-day Reskilling Festival featuring demonstrations, talks, and hands-on instruction. Jim’s website, Rondout Woodworking is a valuable resource for locating working and restored mills.
The International Traditional Knowledge Institute gathers and protects historical knowledge, promotes and certifies innovative practices. Using traditional knowledge does not mean direct reapplication of techniques from the past, but rather seeks to understand the logic of past models of knowledge. It is a dynamic system able to incorporate innovation subjected to the test of the long term and thus achieves local and environmental sustainability.
Lewis Mumford wrote in 1970:
The great feat of medieval technics was that it was able to promote and absorb many important changes without losing the immense carryover of inventions and skill from earlier cultures. In this lies one of it vital point of superiority over the modern mode of monotechnics, which boast of effacing, as fast and as far as possible, the technical achievements of earlier periods.
There are schools and apprentice shops for learning large-scale woodworking skills that are and will be needed for Slow Tech water-driven mills, and wind-driven vessels that will be part of the continuum that supersedes the “blip” of petroleum powered short term thinking and consumption.
The following are some links to the resources, skills, and techniques that are needed to Transition our Bioregion to one that is carbon constrained yet resilient, abundant, and equitable. Let the following list be a starting point – an opportunity to contribute your 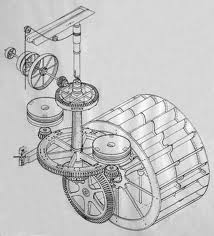 own favorite sites, books, , drawings, and especially experiences with humans with these skills. Perhaps this list can be the beginning of a Bioregional Traditional Knowledge Database that will gather and protect historical knowledge and promote innovative practices based on traditional skills.
own favorite sites, books, , drawings, and especially experiences with humans with these skills. Perhaps this list can be the beginning of a Bioregional Traditional Knowledge Database that will gather and protect historical knowledge and promote innovative practices based on traditional skills.























